What Is Cryptocurrency?
Before buying your first Bitcoin or crypto, let’s get on the same page about what cryptocurrency is.
I’m sure you’ve heard the same boring explanation, it can get complicated, but it doesn’t have to be.
To understand cryptocurrency, let’s first quickly review the basics of “money”.
A Story Of Money
Money is simply a means to acquire goods and receive services, store value, and facilitate commerce.
Money = agreed-upon value by a collective of people
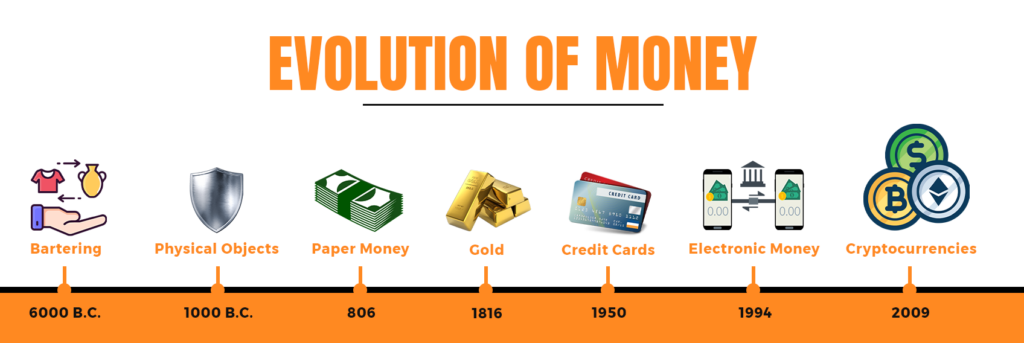
First, we started with bartering as money via physical objects, food or services.
We then graduated to “hard” money, such as gold or silver and then gold coins to make transporting that gold easier.
To overcome issues with gold, we moved into paper money and then linked paper money to “hard” assets such as gold, known as the gold standard.
This brings us to the last 50 years when the gold standard was abandoned in the 1970s, and paper money was no longer backed by “hard money”. We call this the “fiat” money era, and the rapid technological progress of the internet has brought us credit cards and electronic money (such as bank transfers, Apple Pay or PayPal). Many consider cryptocurrencies the next generation and a new form of ‘money’.
Understanding Cryptocurrency
Okay, it’s a new form of money, but what IS it?
Cryptocurrency is a general term for digital or virtual money that uses cryptography for security and is not tied to a specific country or government. Cryptography is just a fancy word for the complicated maths that keeps information secure and secret on computers.
Cryptocurrency is a broad term – you may hear other similar words, such as “crypto-asset”.
The easiest way to understand cryptocurrency is to think of it as “internet native currency or value”. Cryptocurrencies are intended to have no centralising, single party and are managed by many computers working together to ensure no one cheats or spends their tokens twice. So there is no central authority like a government or bank.
Cryptocurrency can include a broad range of activities in the crypto space, such as
- NFTs (unique digital tokens – more on them later)
- Stablecoins (tokens that represent a stable value like the U.S dollar)
- And a wide variety of crypto tokens such as BTC (the largest, most similar to gold), ETH (the second largest, most similar to what you could call an operating system) and a whole host of others that focus on different areas such as gaming, payments or finance.
It’s not important to understand all these different types, but just that there are many and “cryptocurrency” is a broad term that refers to many different digital assets.
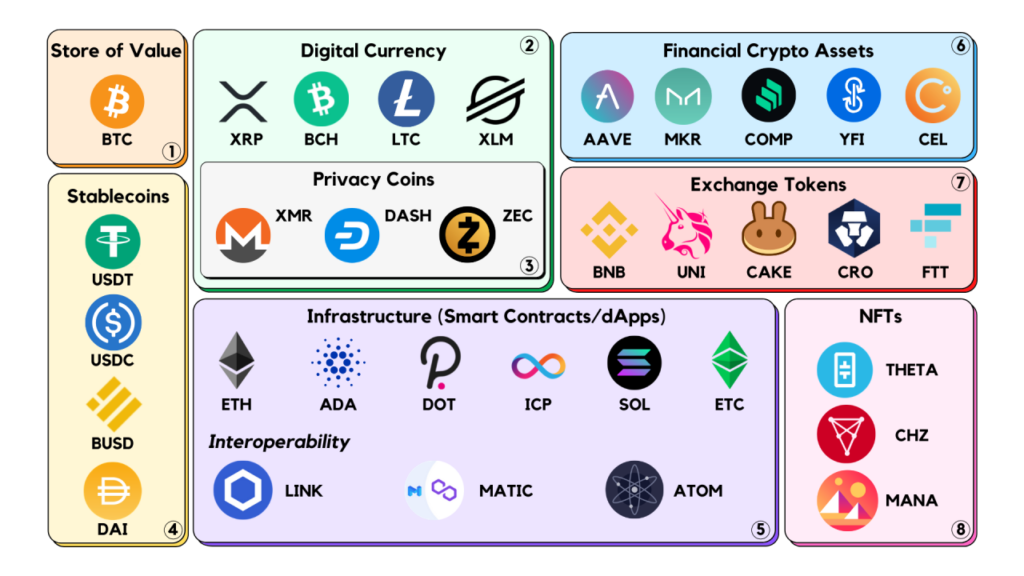
There are thousands of cryptocurrencies out there—because anyone can create one, there is an almost endless amount, with some more trusted than others.
Practical example
Understanding cryptocurrency is best through examples.
The best example of cryptocurrencies is through remittances (sending money overseas via a middleman).
This is extremely costly with “fiat money” and can take time. Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin can be sent directly to the person without using a bank or service provider.
What you NEED to know now
Don’t worry about the different ecosystems and use cases for crypto. We’ll discuss the cryptocurrency ecosystem and these different sectors or uses in a later module.
For the moment, it is important to understand what cryptocurrency is.
- A new form or way to represent digital value or money.
- A broad term that includes a variety of “digital assets” that are secured by fancy math. Bitcoin (BTC) is the biggest followed by Ether (ETH)
- An open system that allows anyone to participate.
- It is secured by a giant network of computers that verify everyone is playing by the rules.
Cryptocurrency Key Points
- Created from code: cryptocurrency is digital money created from code
- Peer-monitored: the cryptocurrency economy is monitored by a peer-to-peer Internet protocol
- Encrypted: cryptocurrency is an encrypted string or hash, encoded to signify one unit of currency


